UBS: The Greek economy stands out in the eurozone with strong growth by 2026
Particularly positive is the image that UBS is outlined for the Greek economy, according to its latest estimates for the period 2024–2026.
With growth rates that exceed the average of the eurozone and inflation in a downward trend, UBS confirms the recovery of the Greek economy, with prospects that stand out on the European map.
Development Momentum, inflation stability and fiscal performance make up an attractive macroeconomic profile. At the same time, however, external imbalances are a key point of attention, intensifying the need to enhance the productive base and competitiveness.
Protagonist Greece in the eurozone
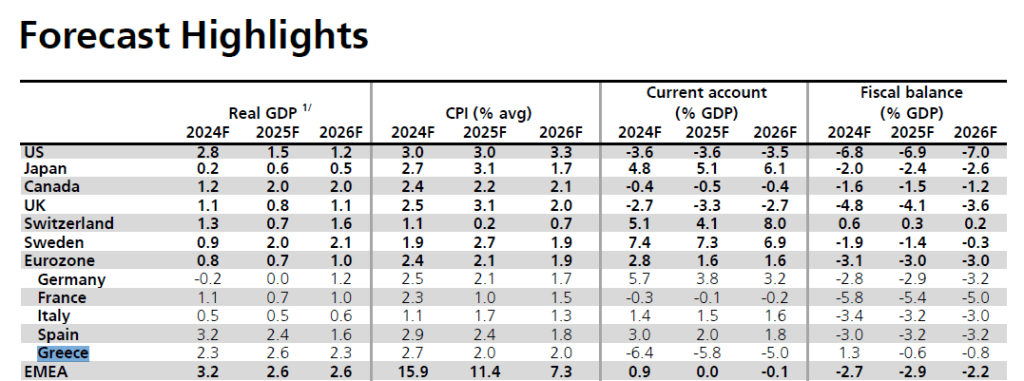
UBS predicts Greek GDP growth by 2.3% in 2024, 2.6% in 2025 and 2.3% in 2026. These performance is clearly higher than the eurozone average, which is expected to record only 0.8% in 2024, 0.7% in 2025 and 1.0% in 2026.
Even stronger economies, such as Germany, are projected to move significantly lower, with growth of -0.2% this year and only 1.2% to 2026. France and Italy are also expected to be subdued (1.1% and 0.5% in 2024 respectively).
Inflation: Fixed Defense
Inflation in Greece is projected to gradually decrease, from 2.7% in 2024, to 2% in 2025 and 2026 – in alignment with the ECB’s target for price stability.
These are levels lower than other European countries, such as Germany (2.5%, 2.1%, 1.7%) and Spain (3.2%, 2.6%, 2.3%).
External Balance: Problem but improved picture
Concerns is raised by a high deficit in the current account balance, which is -6.4% of GDP in 2024, and while gradually decreasing (to -5.8% in 2025 and -5.0% in 2026), it remains one of the highest in Europe. In comparison, Spain maintains a surplus (+1.3% in 2024), and even Italy has positive balances.
This image reveals the country’s structural dependence on imports and the need to boost export activities.
Financial Balance: Relative stability
Greece’s fiscal deficit remains restrained compared to other countries, at -1.3% of GDP in 2024, -1.6% in 2025 and -1.8% in 2026, while the average provision for the eurozone is -3%.
Source: OT







