The Kosmos 482 Soviet probe precipitated on Earth
The satellite designed to reach Venus was trapped in the terrestrial orbit. It weighs 500 kilos and the titanium shell will make it almost intact
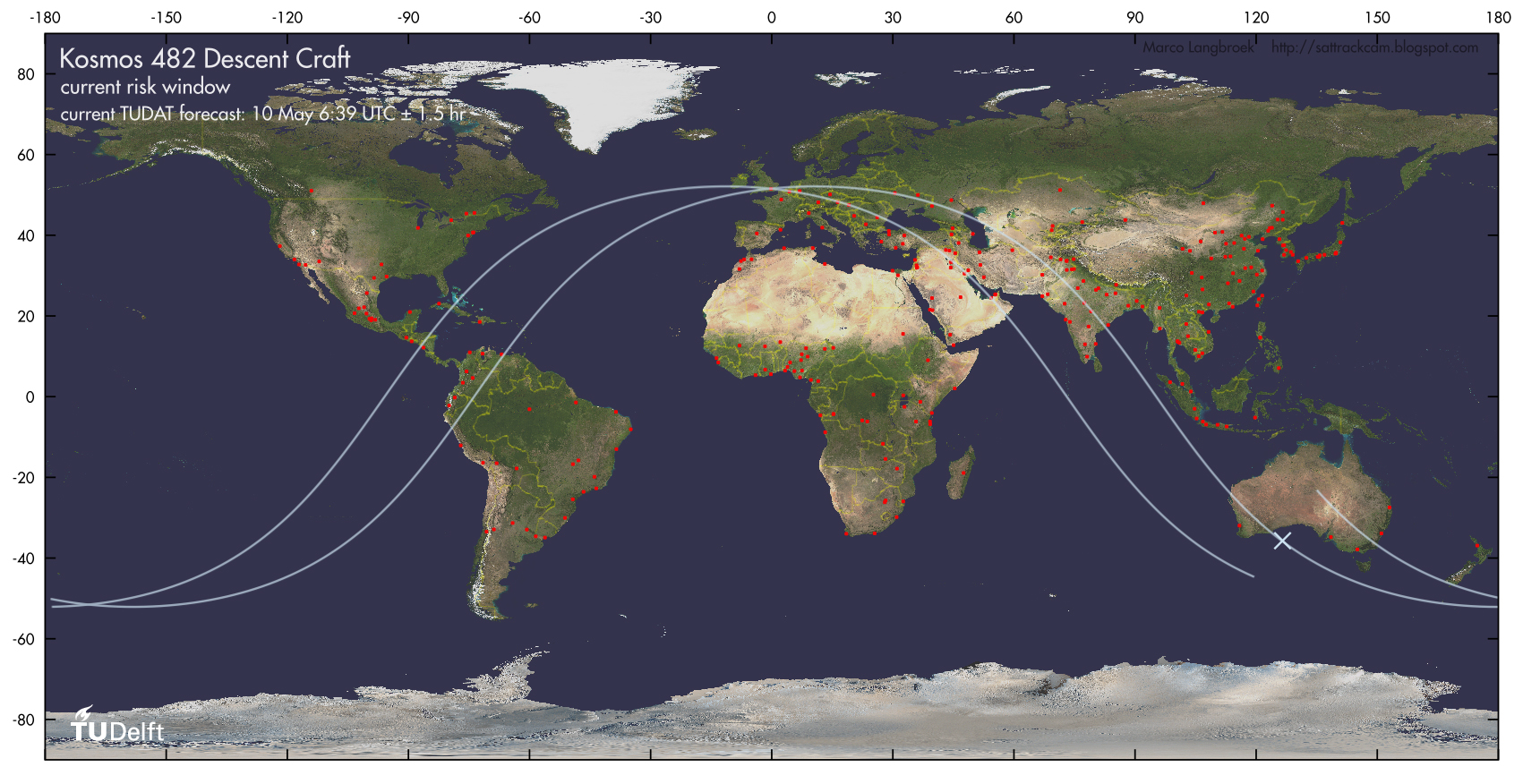
The Kosmos 482 Soviet probe precipitated on Earth. The location of the impact is still unspecified. Some reports report that it has fallen into the Indian Ocean, others on Northern Europe. According to the calculations of the Task Force del European Consortium Space Surveillance and Tracking (EU-SST) The satellite, a heavy 500 kilos with a diameter of one meter, could have fallen on northern Europe.
In Sardinia, the last passage on Italy, which took place on the Tyrrhenian area, had been sighted around 5.00 in the morning while the probe He darted at 28 thousand kilometers per hour. The latest trajectory was instead observed by Germany, from one of the sensors of the EU-SST network. The probe was detected at 8.05 and that point, to have confirmation of the fall, it was preferred to wait the next step on Germany, which however did not happen. This was the
Confirm that the fall has taken place, but at the moment there is no news on the precise place.
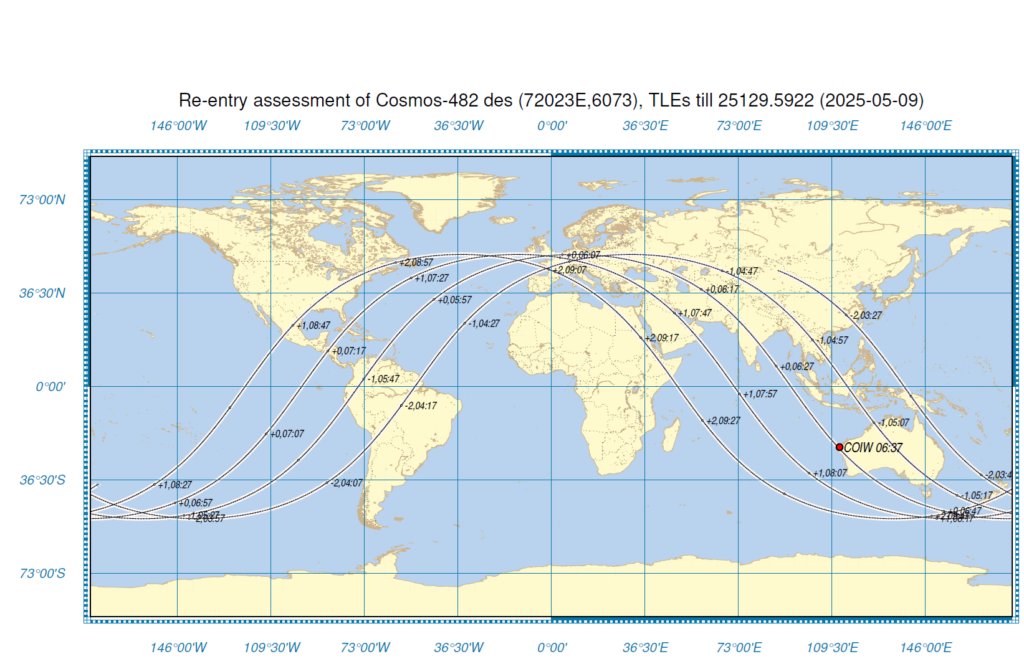
The Russian Space Agency Roscosmos reports that the impact of the Soviet probe Kosmos 482 took place in the Indian Ocean. The descent, writes the Roscosmos on its social networks, was monitored by its automatic alert system for dangerous situation in the nearby space
to the earth.
According to the experts of the agency, the vehicle would be
returned to the atmosphere at 8.24 Italians, in an area at 560
kilometers east of the Central Andamana Island, one of the 3
main islands of the Andaman islands archipelago, in the
southern part of the Gulf of Bengal and fallen into the ocean
Indian west of Jakarta.
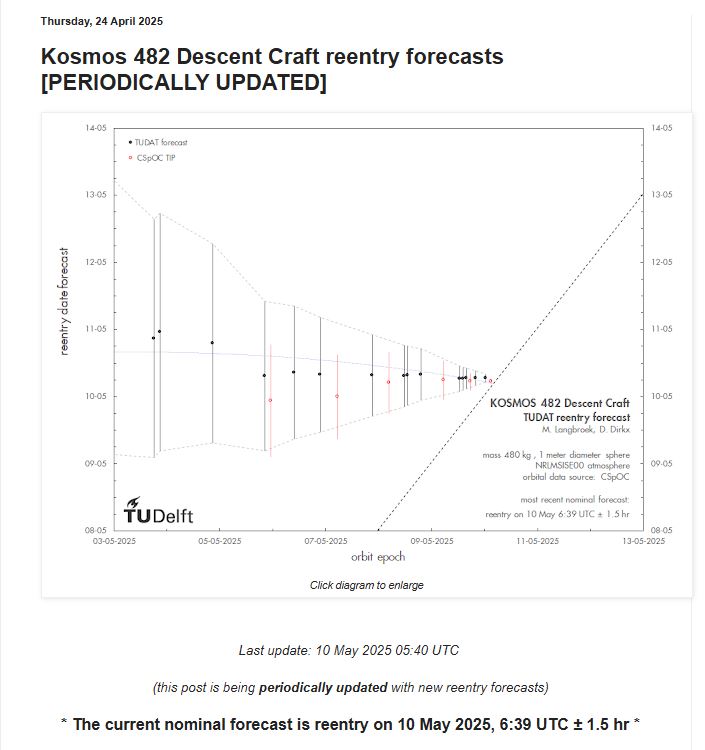
The Kosmos 482 Soviet probe was launched in 1972 to reach Venus But that has never been able to leave the Earth’s orbit, remaining trapped you. In the last few hours he has started his uncontrolled approach to Earth. Taking into account the different estimates of the various space bodies the window within which The probe should have reached the land soil went from 4:05 to 12.47. The uncertainty has clearly depended on numerous variables such as atmospheric density and the solar wind that influenced the return to the atmosphere of an object that moves in an uncontrolled way.
The protective shell in titanium
The Kosmos 482 was launched in March 1972 From the Soviet Union, as part of the Venera missions, which included a series of space probes developed in the USSR to explore and collect data on the Venus planet. Something did not go as expected: the satellite managed to reach the terrestrial orbit, but due to a malfunction of the engine, there was intrapolated there sEnza never leave for his journey to Venus. The probe, designed to resist the infernal heat of Venus, is enclosed in a protective shell in titaniumwill hardly disintegrate completely Upon returning to the atmosphere and it is highly likely that it will reach the earth’s surface almost intact. The parachute on board will probably not work after 53 years of flight.
The risks of the impact
What are the risks? Experts agree that The risks for the population are very low. The earth is a vast target, with a surface mostly covered by oceans and largely uninhabited. Aerospace He writes that although the risk is different from scratch, it is much more likely that a single individual on earth is hit by lightning that being wounded by Cosmos 482. The probability that someone in the world is hit by the object is low, equal to 1 out of 25,000And
considering only Italy the risk is reduced even more,
as he says to Ansa Luciano Anselmospatial dynamic expert
and Associate of Research at the Institute of Science and Technologies
of information `A. Faedo´ del Cnr (Isti-Cnr). « This debris
It is not considered a dangerous object – says Anselmo –
Because the risk that it affects someone is lower than the value
internationally recognized threshold of 1 out of 10,000. There
We then wait that the Lander arrives almost intact to the
earth surfacebecause designed to resist
to the atmosphere of Venus which is much more dense than the terrestrial one,
and this fact paradoxically makes it an object even less
dangerous, because it should not generate fragments».
However, it is a debris that travel in space a
Almost 28,000 kilometers per hour and that, curbed by the atmosphere,
will reach the earth’s surface at a speed of about 200
kilometers per hour. If the impact were to take place on the mainland
Instead of the sea, the effects could vary according to
soil characteristics. “We can expect it to generate a
small crater, or that it can split for the impact »,
adds Anselmo. «The effect would be comparable to that of
A small small car that crashes two hundred per hour ».







