« Hubble » removed the « explosive » galaxy near the Milky Way
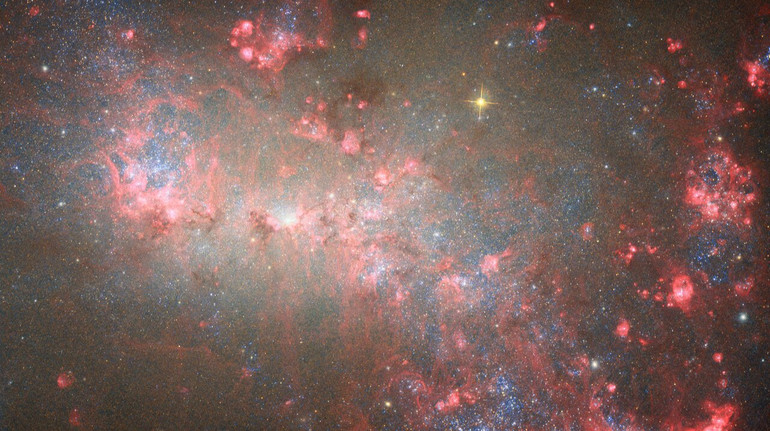

Against the background, many blue stars are visible through dust areas
Photo: ESA/Hubble & Nasa, E. Sabbi, D. Calzetti, A. Aloisi
The Hubble Space Telescope has enlightened the NGC 4449 neighboring galaxy, located in the constellation of hounds of dogs at a distance of only 12.5 million light years from Earth.
She, like our Milky Way, is included in a group of galaxies M94, They tell In the European Space Agency (ESA)
NGC 4449 is classified as a dwarf galaxy: it is much smaller than the Milky Way and contains much less stars.
But despite its compact size, it is extremely active-so much that it is called galaxy-plate (or star-explosive). This term means that the galaxy forms new stars at a higher rate than it is expected for its size.
Unlike most such galaxies, which give birth to stars, the NGC 4449 young bright stars are uniformly uniform. Scientists suggest that such a large -scale plowing process is a consequence of interaction with other galaxies nearby.
The new image of Hubble complements the frame published in 2007 and includes data from several recent observations in different wavelengths. The material collected not only covers the history of the formation of the stars in the NGC 4449, but also helps astronomers to map the most striking and massive stars in more than two dozen neighboring galaxies.
Thanks to the close location of the NGC 4449, it has become an important object to study how galaxies affect each other, and how these interactions can launch new waves of star birth.
James Webba Space Telescope (NASA/ESA/CSA) Watched According to the NGC 4449 galaxy – and showed it even deeper and more in more detail.
Thanks to the hypersensitive infrared devices, the telescope managed to see complex threads of dust gas that stretch through the galaxy. They glow under the action of powerful star radiation, because the NGC 4449 is actively born new stars, and their light literally « lights » the surrounding dust.
Webba observations allow you to study the structure of the galaxy not only in the optical but also in the deeper infrared range. This allows astronomers to understand even better how dawns are born in such galaxies and interstellar structures are formed.
Earlier Hubble He was staring The galaxy that survived the explosion of the Dawn is much more massive than the sun.