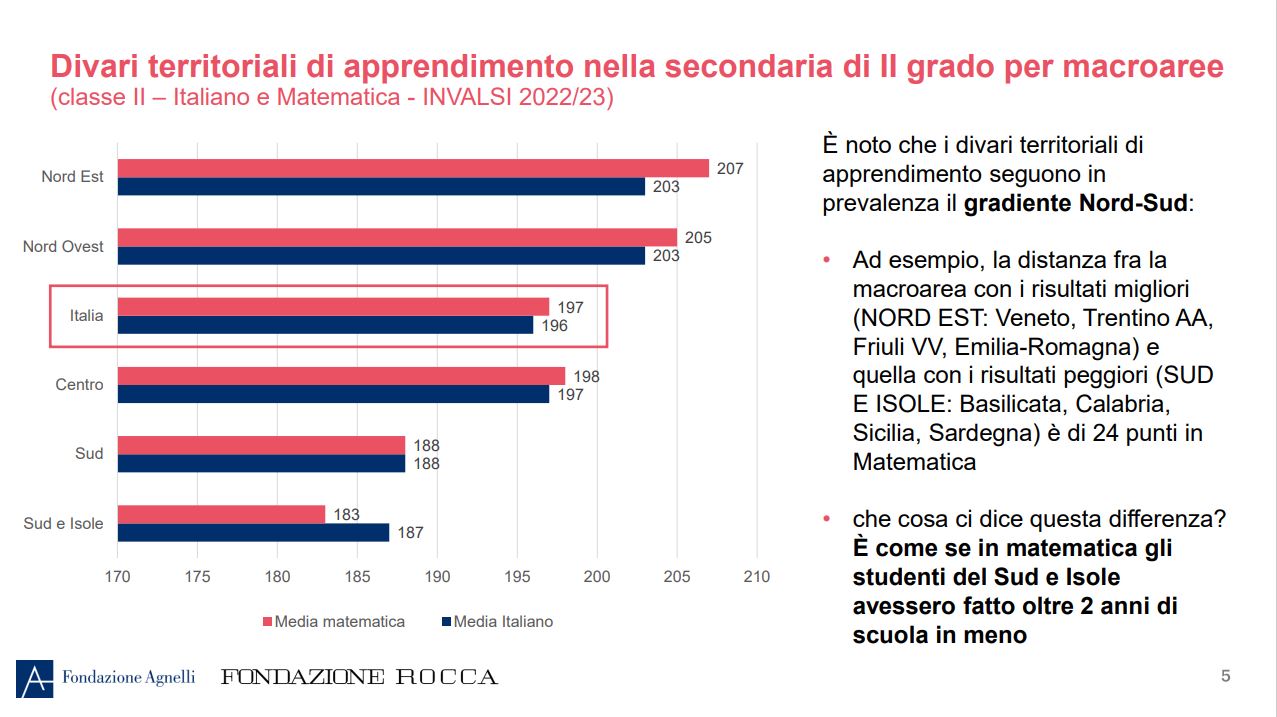
Explosion of a Nova visible in the sky on March 27? What’s true
The protagonist is T Coronae Borealis, a recurring Nova that approximately every 80 years becomes thousands of times brighter than the sun. A French astronomer has hypothesized a precise date, but there are no certainties that will be the right day: it could be in November but also in 2026 or 27
On March 27 will explode a star (or rather, a Nova) and can we see it by the naked eye in the certain? The date is suggestive, but the scientific reality is more complex. The protagonist of the matter is T Coronae Borealisalso nicknamed « Blaze Star » (flaming star) for its ability to suddenly increase brightness. A phenomenon, known as Nova applicant, which takes place on average every 80 years. The latest explosions recorded with certainty took place in 1866 and 1946, and there are also hypotheses on 1217 and 1787, although historical documents are less precise.
What is T Coronae Borealis
T Coronae Borealis is a binary system located about 2,600 light years from the earth, formed by a white dwarf and a red giant. The white dwarf, extremely dense and compact, subtracts material from the red giant companion thanks to its strong gravity. This accumulated gas deposits on the surface of the white dwarf, gradually increasing temperature and pressure until it reaches a critical threshold. In these extreme conditions, Sudden explosive reactions are triggered that make the star shine hundreds of thousands of times more intensely than the sun. To the point that the star also becomes visible to the naked eye for a few days or weeks. It is important to underline that this explosion does not destroy the white dwarf: the phenomenon takes place only on the surface, leaving the star intact and ready to repeat the cycle in the future.
Where the date of March 27, 2025 is born from
The prediction is not the result of some conspiracyers with unbridled imagination. The date of March 27 derives from a recent research published by the astronomer Jean Schneider of the Paris Observatory. Schneider analyzed the historical dates of the past explosions by combining them with the orbital period of the binary system, which is approximately 228 days. His hypothesis is based on the observation that the explosions seem to take place in particular moments of the orbit, even suggesting the possible influence of a third celestial body not yet discovered, with a possible ternary system (and with the problem of the three bodies).
Schneider’s hypothesis
Recent studies have noticed significant variations in the brightness and activity of the binary system, which recall phenomena observed in others Novae Just before their explosion. However, the same research invites prudence: the previous eruptions did not take place with a perfect punctuality, showing variations of over a year compared to the expected periodicity. In short, it is Schneider himself who puts his hands forward: there are no certainties that the explosion will take place on March 27. It could happen in other dates proposed by the French scientist, such as November 10, 2025. Or even in June 2026 or at the beginning of 2027.
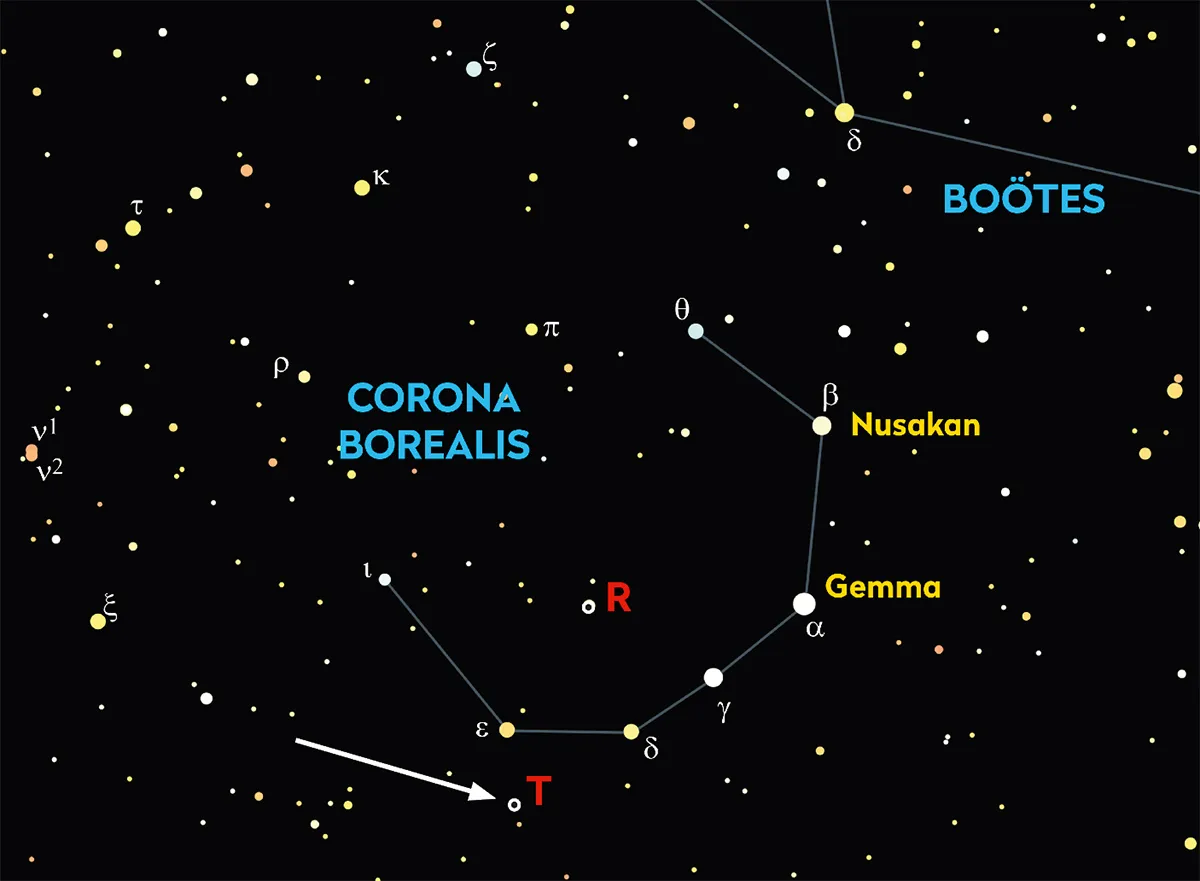
A rather large window, therefore. With a single certainty: when it will explode, This star will illuminate the constellation of the boreal crown for a few daysbecoming one of the brightest objects in the night sky. How to see it, when the explosion will happen? T Coronae Borealis is found in the constellation of the boreal crown, visible in the sky of the north hemisphere. To find it you have to look for a group of semicircle or crown stars located between the constellations of Hercules and Boote (Above find a celestial map developed by Pete Lawrence for BBC). The boreal crown is clearly visible in spring and summer, especially between April and July, looking towards the east/north-east in the early hours of the night. When T Coronae Borealis will explode like Nova, it will suddenly become so bright that it is easily identifiable to the naked eye, shining with a brightness comparable to that of the polar star.