A bat flies ‘Knoerthard the North Sea’ and then comes across a wind farm
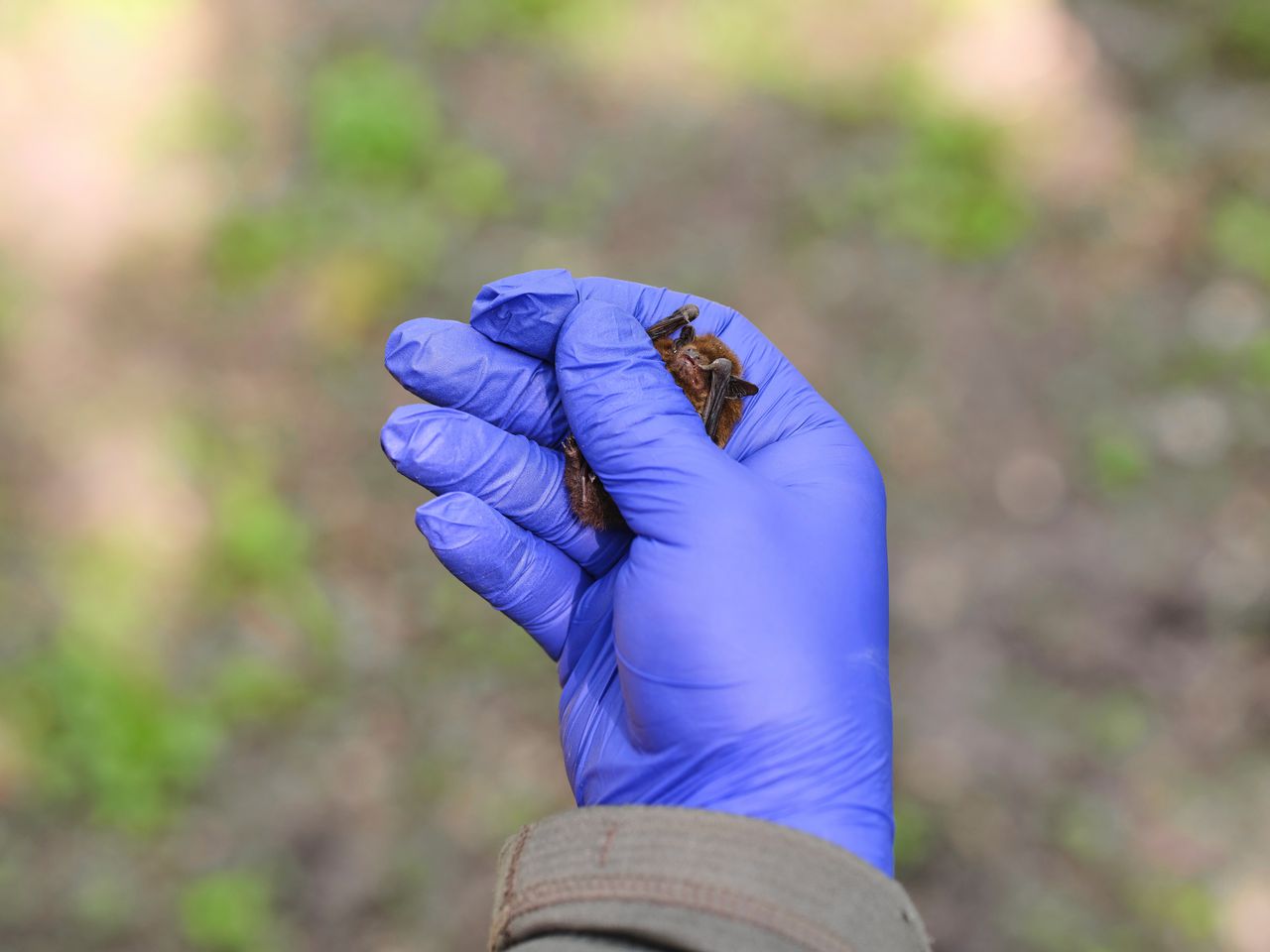

The rugged dwarf bat, a woolly animal that easily fits in a palm, sometimes ventures over the North Sea. There, offshore wind farms pose a threat to the bat, but there is too little knowledge to prevent victims. In 2021 and 2022, researchers from Wageningen University & Research followed 44 rugged dwarf bats – the most common bat species in the North Sea – during their migration from the English east coast to the European mainland. Ecologist Sander Lagerveld (56) talks at the Wageningen Marine Research in Den Helder about the bat migration research, which recently Movement Ecology It appeared: « They pop over the North Sea with wind – they are across the street in three to five o’clock. »
Not all bat species migrate, but the rugged dwarf bat (Pipistllus nodhusii) is a real long -distance puller who can travel more than two thousand kilometers. In the spring the females fly to Northeastern Europe to get boy, in the fall they return to the warmer Southwest Europe to hibernate there. The males migrate over shorter distances. And some bats even venture to England.
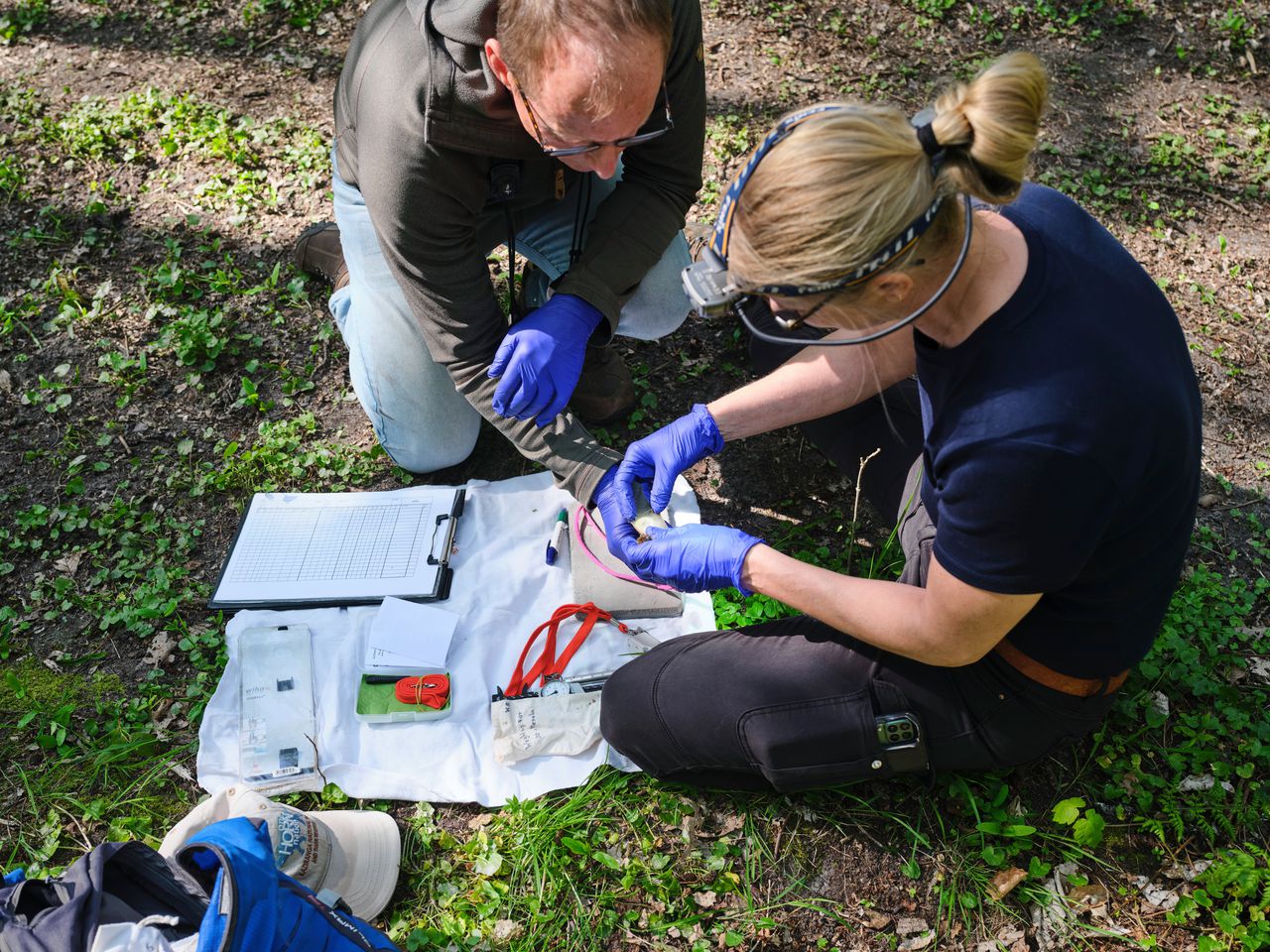
Colleagues from Lagererveld stuck a transmitter of only 0.26 grams on the English east coast and a mini antenna on 44 bats. Reception stations along the North Sea coast catch the radio signals of the individual bats so that the researchers can see where they fly. The research is part of WOZEP, a national research program into the ecological effects of wind turbines at sea. It is risky for a bat to cross the North Sea, Lagerveld says. « There are few places to hide, food is scarce. They therefore try to avoid a crossing first, shows our research. So they fly along the coast – exactly where there are many wind turbines. If they cannot avoid the sea, they choose the shortest route. And they are waiting for wind, then they can reach gigantic ground speeds that we have detected is 60.5 per hour.” ”” ””.
How fast does a bat normally fly?
« Half as fast, about twenty -five kilometers per hour. The wind determines everything. The moment they have a wind, they also fly slower to save energy. And with side wind they fly harder to not blow out too much. With Meewind they can fly hundreds of meters high, possibly even two and a half kilometers – but with less good conditions they usually usually fly.” ””
How many bats victims make wind turbines at sea?
« We don’t know that, we can’t measure that yet: if a victim falls there, you will immediately lose him. With wet finger work, an estimate of one bat per wind turbine per year, on land is usually assumed from five to ten. In Germany it is estimated that a quarter of a million bats are becoming victims a year. It is a serious ecological problem. »
One per year does not sound like a lot.
« Nevertheless, wind energy at sea may be a threat to the population of rough dwarf bats, if all offshore ambitions of thousands of wind turbines in the North Sea are realized. According to recent German research, the genetic diversity of the species seems to be taking. And that means that the population is probably already becoming smaller. »

How big is the population now?
« We don’t know that. Population monitoring is being done, but only a trend comes out. With a migrant species it is also difficult to measure because of the seasonal appearance and a huge distribution area: they are far in Russia. »
What do you like the best finding of the research?
« We have developed a new way to calculate the flight height and speed in three dimensions, from two -dimensional data. As a researcher you are always uncertain whether you are doing well. So when we saw that our calculation yielded flying speeds that beat with previous tests in the wind tunnel, the flag went out. »
That calculation is based on five individuals who made the crossing in one night. That’s pretty little.
« We can’t build a model on that, no. But we do think that here is the crux for mitigation: by looking very well at the relationship between wind speed, wind direction and fly height. This was the first time it became so clear. The same laws are valid for bats as for birds, which we have been doing so much of course. protect. ”
I am an ecologist, so I love animals intrinsically, but birds are more my hobby
How can you protect bats against windmill wings?
« The first way is a bit of an open door: put wind farms down in places with few bats. Avoid coastlines, for example. Stopping the windmills If many bats are expected, it is also possible, with Windpark Borssele and at many wind farms on land that already happens. A third possibility is already hiding bats by, for example, their Sonar.”
Where does your interest in migrating bats come from?
“I have been a fanatic bird puller since I was ten. Then we moved to the coast, to Camperduin (near Schoorl). There people with binoculars count the sea bird pull very closely every hour, all year round. I spent my whole childhood there. Occasionally bats came from sea. I found them roughly. Seen at sea then I started the investigation. «
Do you also like bats?
« I am ecologist, so I love animals intrinsically, but birds are more my hobby. During the weekend I will watch birds rather than bats. Bats are more my work. »

/s3/static.nrc.nl/images/gn4/data131805069-169c64.jpg)
/s3/static.nrc.nl/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/02142337/data131661267-e5c10d.jpg)
/s3/static.nrc.nl/images/gn4/stripped/data131801801-6edbde.jpg|https://images.nrc.nl/NnMBum-tvrss6HVN9ZGF1CulyXo=/1920x/filters:no_upscale()/s3/static.nrc.nl/images/gn4/stripped/data131801801-6edbde.jpg|https://images.nrc.nl/pC5-NDDiyZY09ONTozVCZqdZIV4=/5760x/filters:no_upscale()/s3/static.nrc.nl/images/gn4/stripped/data131801801-6edbde.jpg)